Gynecomastia Treatment in Singapore
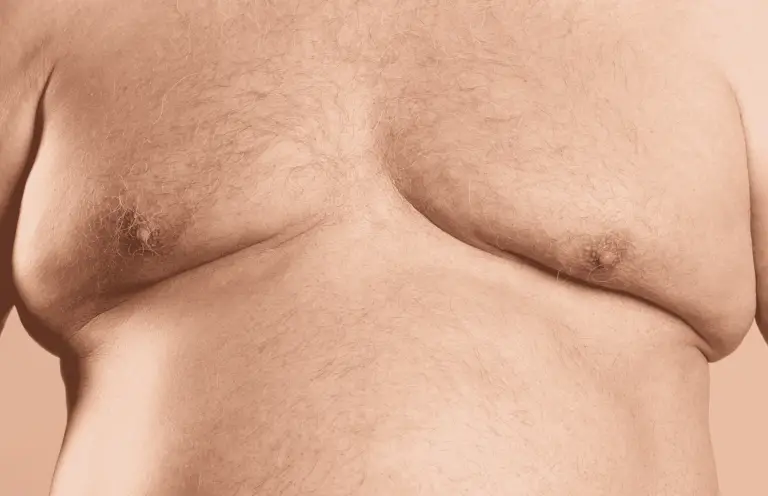
Gynecomastia is a common condition where males develop enlarged breast tissue. This is common in infancy, adolescence and in middle-aged to older males.
Gynecomastia is often benign and related to sex hormone changes, which are associated with normal physiology. Physiological gynecomastia is common and has a trimodal distribution in neonatal, pubertal and older males.
While it is benign, it can affect appearance, confidence, and overall quality of life. Individuals who experience persistent or worsening gynecomastia may require medical evaluation to rule out underlying medical conditions.
At LG Endocrinology, we offer a thorough assessment to identify both the physical and hormonal factors contributing to gynecomastia. If you are concerned about persistent breast enlargement, our clinic provides discreet, personalised, and evidence-based care to help you understand your condition and explore suitable treatment options.
What Is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of male breast tissue due to an increase in glandular tissue. The condition is common among adolescents, adults, and older men. This is different from pseudogynecomastia, which appears similar but is caused by excess fat rather than true glandular growth.
In Singapore, clinicians have observed a growing number of men in their 20s to 30s seeking treatment for gynecomastia. Although there are no official national statistics, international studies suggest that up to 60% of men worldwide experience gynecomastia to some degree. Many of these cases occur without any identifiable cause.

What Are The Causes of Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia can develop for many reasons, most of which relate to changes in hormone levels. In Singapore, individuals often experience this condition due to a mix of biological, medical, and lifestyle factors. Below are some key causes:
- Hormonal imbalance: An imbalance between oestrogen and testosterone is the primary driver of gynecomastia.
- Puberty: Hormonal fluctuations during adolescence can cause temporary breast tissue enlargement.
- Ageing: Testosterone levels naturally decline with age, increasing the likelihood of breast tissue growth.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as anti-androgens, chemotherapy drugs, some heart medications, anti-anxiety drugs, anti-stomach ulcer drugs, and antibiotics, can contribute to breast enlargement.
- Medical conditions: Issues like thyroid disorders, liver disease, kidney disease, or testicular problems can disrupt hormone levels and lead to gynecomastia.
- Lifestyle factors: Obesity, alcohol consumption, and illicit drug use may also cause the development of gynecomastia.
- Supplements and steroids: Anabolic steroids and some bodybuilding supplements may interfere with hormone balance and trigger breast tissue growth.
What Are The Symptoms of Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia may present with:
- Enlargement of one or both breasts
- Puffiness around the nipple area
- Tenderness or sensitivity of the nipples
- A firm disc or lump directly beneath the areola
- Noticeable asymmetry or swelling between sides
- Nipple discharge
When should I see a doctor for gynecomastia?
You should seek medical evaluation if the enlargement persists or continues to worsen, especially if you notice:
- Persistent or worsening breast enlargement
- Pain, swelling or tenderness
- A lump beneath the nipple or elsewhere in the breast
- Nipple discharge
- Rapid changes in size or skin abnormalities
Feeling worried about your appearance or experiencing emotional distress is also a completely valid reason to reach out for medical support. If these concerns are affecting your confidence or quality of life, book an appointment with Dr Gani to receive a personalised consultation.

How Is Gynaecomastia Diagnosed in Singapore?
Gynaecomastia is diagnosed through a structured approach that assesses medical factors, hormonal health and breast tissue characteristics. Evaluation may involve a medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging and targeted investigations to clarify the cause and exclude uncommon conditions.
A detailed history is the first step in diagnosing gynaecomastia. Reviewing your medical conditions, medications, supplements and lifestyle factors helps identify possible contributors to glandular breast growth. The onset, duration and any associated symptoms are also discussed to determine whether the enlargement is stable, progressive or related to puberty.
A physical examination helps distinguish true glandular gynaecomastia from fatty enlargement. This typically involves assessing:
- The presence of a firm disc of glandular tissue beneath the areola
- Whether one or both sides are affected
- Skin changes or nipple discharge
- Signs of hormonal imbalance, such as reduced body hair or testicular abnormalities
- Any hard or irregular lumps that may require further investigation
If a hormonal imbalance is suspected, blood tests may be performed. These can assess testosterone, oestrogen, thyroid function and other endocrine markers. Additional tests, such as liver, kidney and lipid profiles, may be ordered to evaluate systemic conditions that can contribute to gynaecomastia.
Imaging is helpful when the diagnosis is uncertain or when certain features need closer assessment. A breast ultrasound is commonly used to evaluate the type and pattern of tissue, while a mammogram may be recommended if there are suspicious findings or when rare causes need to be ruled out.
Note:
Although uncommon, male breast cancer must be excluded when hard, fixed or concerning lumps are present. Imaging and further diagnostic tests help ensure that any unusual findings are evaluated promptly and thoroughly.
What Are The Treatment Options For Gynecomastia in Singapore?
Gynecomastia management may include monitoring, medication, or lifestyle adjustments. Oftentimes, multiple management strategies are used together to ensure that both glandular growth and contributing factors are properly addressed.
Mild or puberty-related gynaecomastia may resolve without intervention. Doctors may recommend periodic reviews, although long-standing puberty-related gynaecomastia that persists for more than 24 months is less likely to resolve on its own.
Certain medications can help regulate hormone levels when appropriate. Medications that have been studied for the treatment of gynecomastia include Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs), testosterone (only for males with hypogonadism), and aromatase inhibitors. Tamoxifen is the preferred SERM that is typically used.
If a specific drug is identified to be causing gynecomastia, switching or discontinuing it under medical supervision may reduce symptoms. Treating underlying medical conditions, including hormonal or metabolic disorders, can also improve gynaecomastia.
Weight loss may help when the enlargement is due to excess fat rather than true glandular growth. Reducing alcohol intake or recreational drug use may also lower the risk of progression. It is important to note that some supplements can contribute to hormonal imbalances and should be reviewed with a healthcare professional.
Gynecomastia surgery removes excess glandular tissue, fat or both. Techniques may include liposuction, gland excision or a combination of these approaches. At LG Endocrinology, we work with other surgical specialities to recommend these procedures if indicated.
Our Trusted Endocrinologist
Dr Linsey Gani
Consultant Endocrinologist
MBBS (Aust), B Med Sci, FRACP (Endocrine), FAMS (S’pore), MPH (Harvard), Clinical Assistant Professor (Duke-NUS Medical School)
Languages: English, Mandarin, Bahasa Indonesia
Dr Gani is a skilled endocrinologist with experience guiding gynecomastia management. She is a fellow of the Royal Australian College of physician and the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.
Why Choose Us?

Every individual’s condition and goals are different. Dr Gani designs customised management plans that may include hormonal evaluation, medical treatment, lifestyle guidance, or surgical referral when appropriate.

We evaluate both breast tissue changes and the underlying hormonal, metabolic, or health factors that may be contributing to gynecomastia, ensuring a complete and accurate diagnosis.

We understand that gynecomastia can be a sensitive concern. Consultations with Dr Gani are conducted with professionalism and discretion to help you feel at ease throughout your visit.
FAQs About Gynecomastia
Will gynecomastia recur?
No, it is uncommon for gynecomastia to recur. In most cases, the breast tissue does not grow back once the underlying cause has been treated. Weight gain can make the chest appear fuller again, but this usually improves with weight loss. However, if gynecomastia was originally triggered by ongoing medication or substances, it may return if those medications or substances are continued.
Do chest exercises help gynecomastia?
Chest workouts can strengthen and shape the pectoral muscles, which may improve overall chest contour, but they cannot eliminate true glandular breast tissue. This means the underlying gynecomastia will still be present. For noticeable or persistent gynecomastia, medical treatment is usually the most effective option, depending on the severity.
Is gynecomastia a serious condition?
Gynecomastia is generally not dangerous, as it is a benign enlargement of breast tissue. However, it can cause tenderness or discomfort in some individuals, and the change in chest appearance may impact self-confidence.
Persistent or worsening gynecomastia should be medically evaluated to rule out underlying medical causes. When the symptoms begin to affect daily life, an evaluation can help determine the cause and guide appropriate management.
Disclaimer
This information is provided for general education. It does not replace personalised medical advice. Please consult your doctor for guidance on the medications that may be appropriate for you.
Book an Appointment
Fill out the form below to schedule your appointment.
Dr. Linsey Gani Endocrinology
10 Sinaran Drive, #10-08, Novena Medical Center, Singapore 307506
+65 6397 7101
+65 9128 7480
Monday - Friday
08:30 - 12:30
Monday - Friday
14:00 - 17:30
Saturday
09:00-12:00
Sunday & Public Holiday
Closed
Monday - Friday
08:30 - 12:30
14:00 - 17:30
Saturday
09:00 - 12:00
Sunday & Public Holiday
Closed
